반응형
And &&
→ 좌항과 우항의 값이 모두 true일 때 참이 됨
package sujin.conditionaloperator;
public class AndDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
if (true && true) {
System.out.println(1);
}
if (true && false) {
System.out.println(2);
}
if (false && true) {
System.out.println(3);
}
if (false && false) {
System.out.println(4);
}
}
}
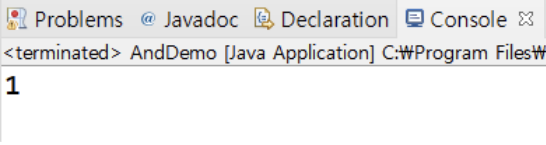
▶️ 첫 번째 조건문에서 좌 우항 모두 true이기 때문에 결과값은 1
로그인 프로그램 응용
package sujin.conditionaloperator;
public class LoginDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String id = args[0];
String password = args[1];
if (id.equals("Gwak") && password.equals("sujin")) {
System.out.println("right");
} else {
System.out.println("wrong");
}
}
}→ if 중첩문을 사용했을 때보다 비교적 간편하게 표현 가능
Or ||
→ 좌우항 중 하나라도 true면 모두 참이 됨
package sujin.conditionaloperator;
public class OrDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
if (true || true) {
System.out.println(1);
}
if (true || false) {
System.out.println(2);
}
if (true || true) {
System.out.println(3);
}
if (false || false) {
System.out.println(4);
}
}
}
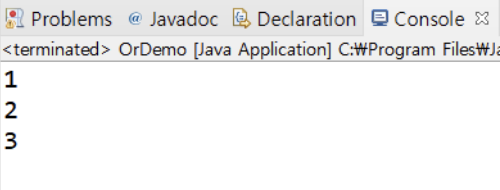
▶️ 좌우항 모두 false인 경우를 제외한 결과값이 모두 출력됨
로그인 프로그램 응용
package sujin.conditionaloperator;
public class LoginDemo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String id = args[0];
String password = args[1];
if ((id.equals("Gwak") || id.equals("egoing") || id.equals("k8805"))
&& password.equals("sujin")) {
System.out.println("right");
} else {
System.out.println("wrong");
}
}
}▶️ id에 Gwak, egoing, k8805 셋 중 하나라도 맞으면 참이고 password에 sujin이 맞으면 right, id나 password 둘 중 하나라도 거짓이면 wrong을 출력함
Not !
→ !는 부정의 의미로, true 앞에 붙이면 false, false 앞에 붙이면 true가 됨
package sujin.conditionaloperator;
public class NotDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
if (!true) {
System.out.println(1);
}
if (!false) {
System.out.println(2);
}
}
}
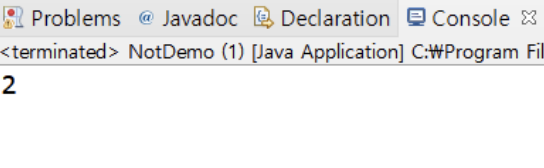
▶️ !true는 false이기 때문에 1은 출력되지 않고 !false 즉 true인 결과값 2만 출력됨
반응형
'Language > Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [ Java ] 배열 (0) | 2021.09.03 |
|---|---|
| [ Java ] 반복문 (0) | 2021.09.03 |
| [ Java ] 조건문 (0) | 2021.09.03 |
| [ Java ] 연산자 (0) | 2021.09.03 |
| [ Java ] 데이터 타입 (0) | 2021.09.03 |